Authenticating Sencha Web Application Manager via ForgeRock’s OpenDJ
Jakub Janoska
9 years ago
I am going to show how to integrate two impressive technologies: 1. Sencha Web Application Manager (SWAM), that is an application platform for deploying and managing web and mobile apps and 2. ForgeRock OpenDJ open-source LDAP directory server.
Sencha SWAM is an enterprise software product for deploying and managing HTML 5 applications, which are accessible from Windows Desktop, iOS, Android and Windows Phone clients. Most of today’s enterprises use web and mobile applications to support their business. Deployment and management of these apps easily becomes a nightmare, when considering the number of browsers, desktop and mobile platforms that they are expected to run on. Sencha SWAM eases deployment and management through a central management interface, makes it faster, more secure and gives better control over the set of deployed applications, devices and users through advanced reporting and analytic capabilities.
Authentication is key to security of mobile and web applications. Sencha SWAM offers several solutions for authentication. Integration with an LDAP directory is one of the fundamental options. This article shows, how to integrate Sencha SWAM with ForgeRock OpenDJ, but you can use any other LDAP solution.
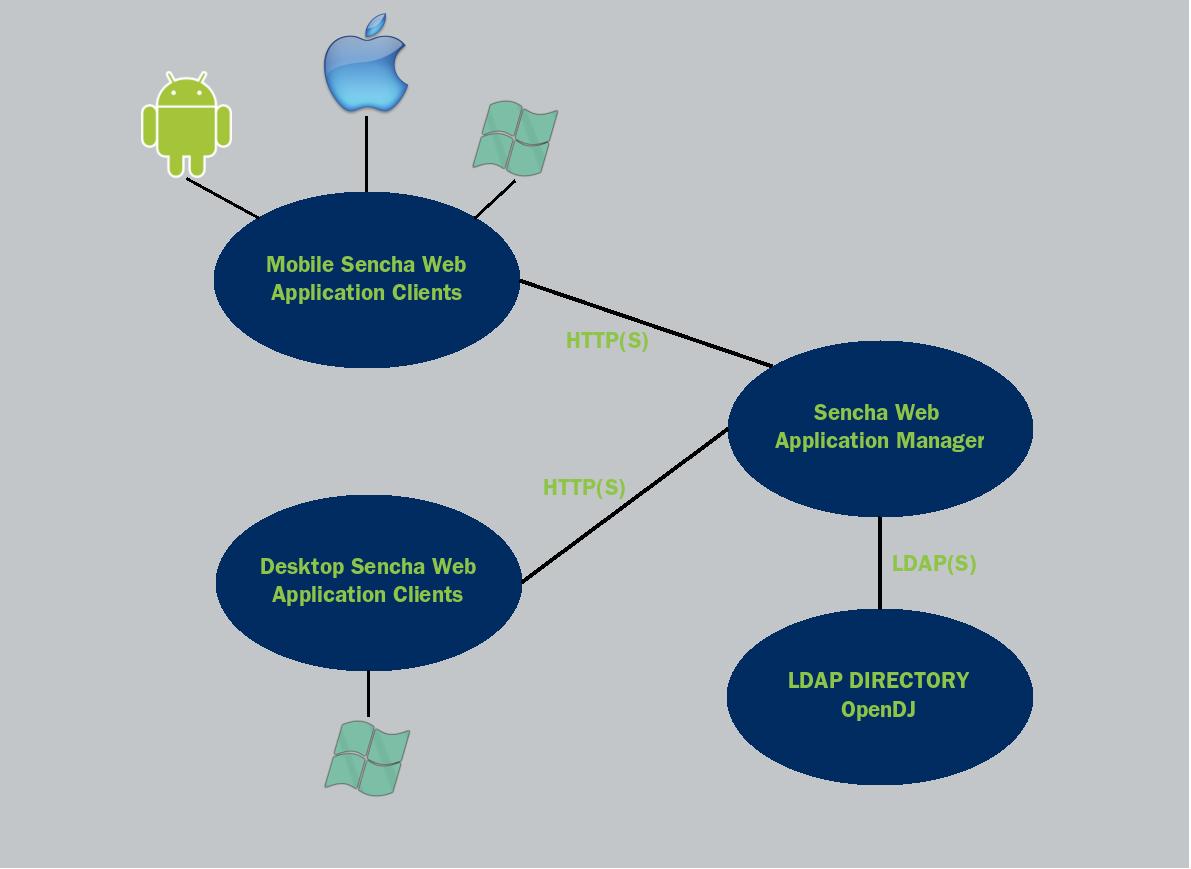
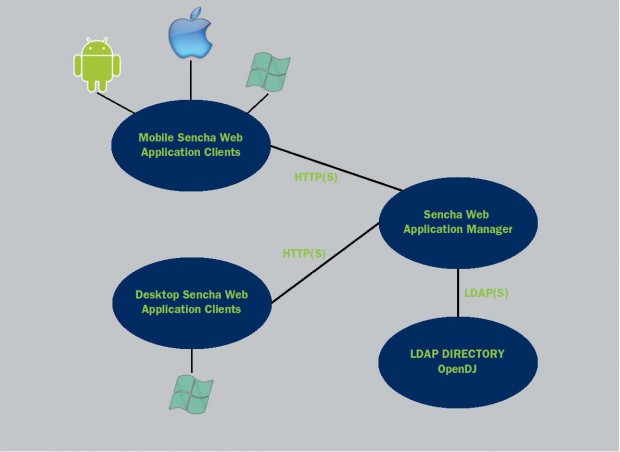
The following diagram gives some clues of how these technologies are tied together.
The installation process of OpenDJ was described in our previous blog in detail, I only add a download link to the .zip distribution of OpenDJ.
Configuring OpenDJ
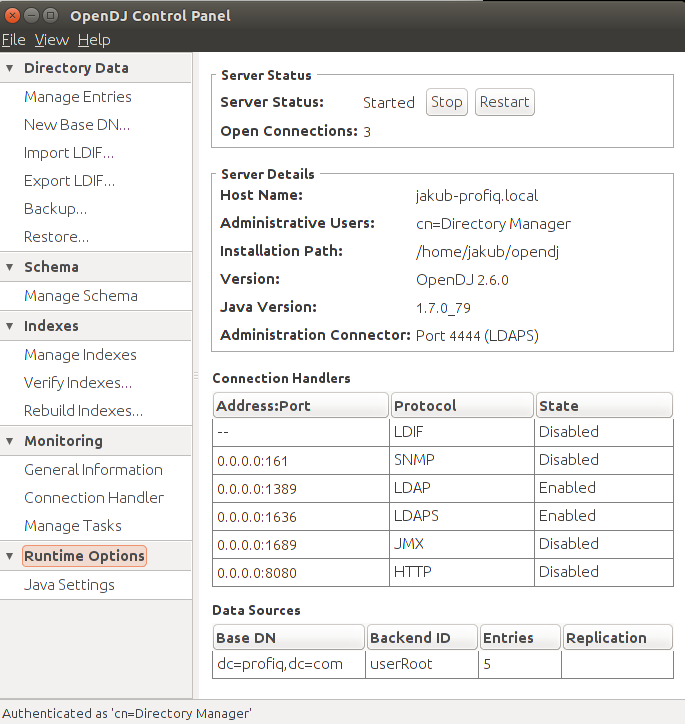
We can use the CLI or the graphical Control Panel for configuration once we are done with the installation. This is how the Control panel of ForgeRock OpenDJ looks like:
Here is an initial set of commands that you will need, when administering ForgeRock OpenDJ:
- Start OpenDJ:
./bin/start-ds - Stop OpenDJ:
./bin/stop - Launch Control Panel (GUI):
./bin/control-panel - For additional details check out the documentation
Example of output records:
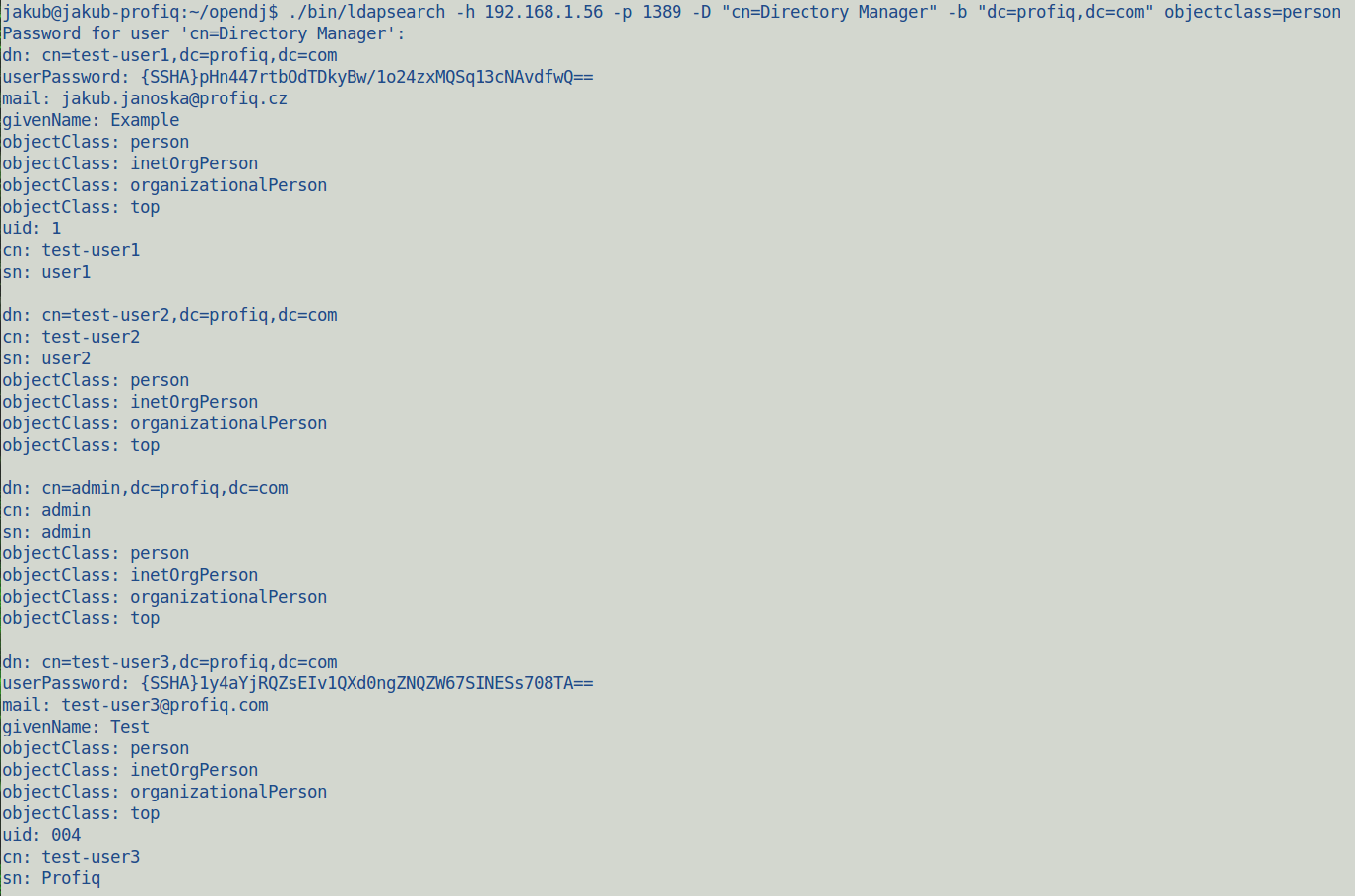
- Get your users via CLI
./bin/ldapsearch -h 192.168.1.56 -p 1389 -D "cn=Directory Manager" -b "dc=profiq,dc=com" objectclass=person
- Output example of 3 records:
The figure shows attribute names used by ForgeRock OpenDJ. dn, cn, sn, uid and mail are the most important attributes for mapping values to Sencha SWAM.
SWAM (Sencha Web Application Manager)
The server side of SWAM is available as a cloud service and has an on-premises distribution too. This article talks about the cloud version. To access the cloud version, you have to register on this form (see Figure 4) and then you will receive invitation email.
You are ready to start using Sencha Web Application Manager now. You can deploy web applications based on Sencha Ext JS or other HTML5 frameworks.
Mapping attributes
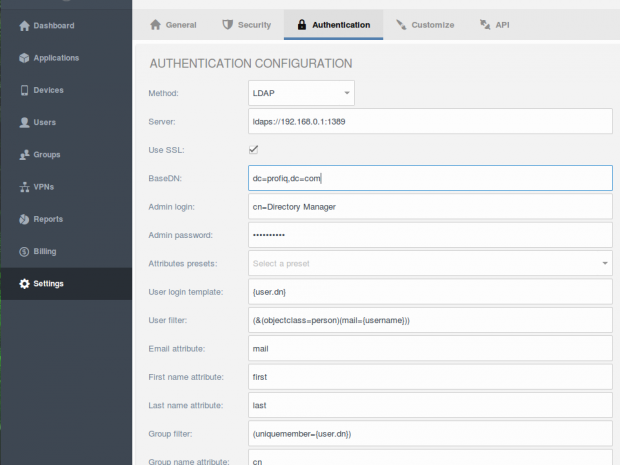
Here is a specific example of setting your mapping attributes to LDAP attributes after you logged in to Sencha SWAM, based on LDAP attributes that we have shown above.
This configuration is variable to a certain extent. You can use a different filter, for example (&(objectclass=person)(uid={username})) instead of (&(objectclass=person)(cn={username})). These determine the attributes that will be used for logging in to Sencha SWAM.
At this point, your Sencha Web Application Manager is configured to use ForgeRock OpenDJ (LDAP) authentication. You don’t have to create accounts and groups within SWAM anymore. It will automatically use accounts configured in ForgeRock OpenDJ instead.
The complete functionality of Sencha SWAM is described in Sencha’s documentation.